Cathodic Protection of Precast, Prestressed Multistory Car park Slabs, using a Surface Applied Galvanic Zinc Layer Anode.


A surface applied galvanic Zinc Layer Anode (ZLA) system was installed onto a multistory carpark structure to provide cathodic protection to the soffits of the prestressed hollow concrete slabs, which were suffering from chloride induced corrosion deterioration.
A surface applied galvanic anode system was selected to provide cathodic protection, as this offered a low risk of exceeding the hydrogen embrittlement potential and provided a unique application approach, which was compatible with the hollow slab construction.
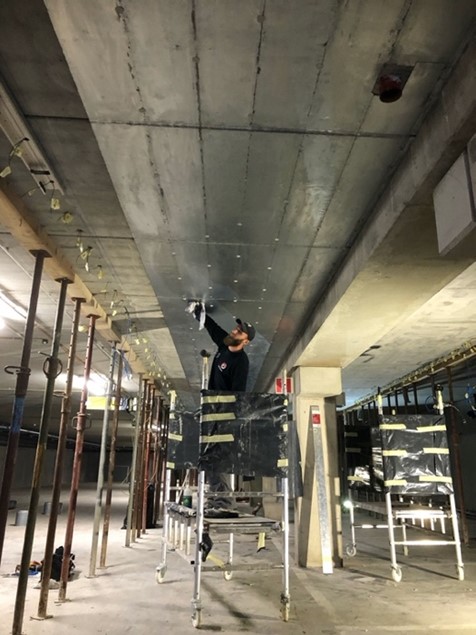
The ZLA system consists of a high purity zinc foil, complete with an ion-conductive, auto moistening, humectant/activator/adhesive layer (gel), designed to be surface mounted onto the surface of concrete structures.
During the pilot phase, a total of 40 m2 of ZLA was applied onto two anode zones and monitored for a month, to prove concept and system performance. Following the pilot phase, the remainder of the cathodic protection works were completed, extending to 320 m2 concrete.
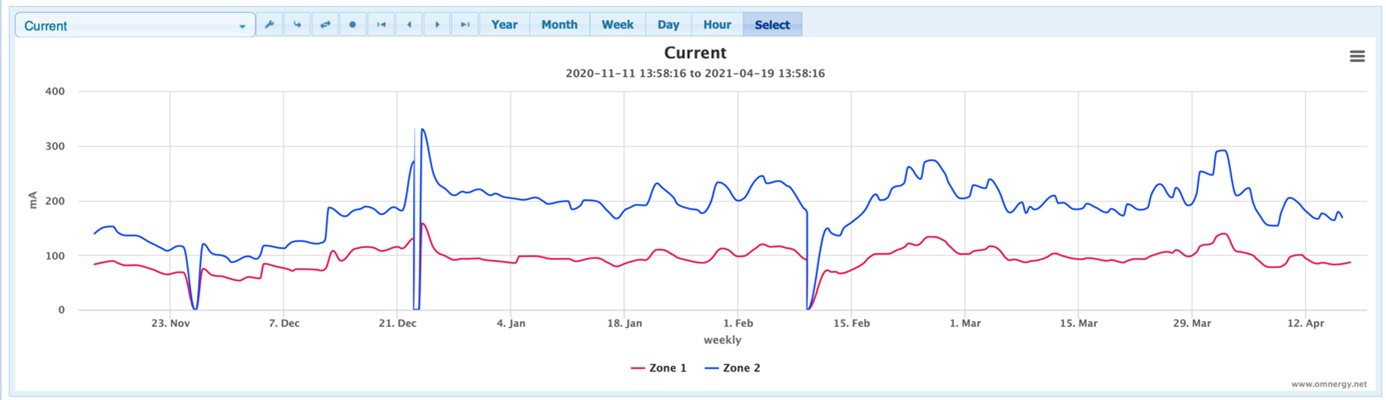
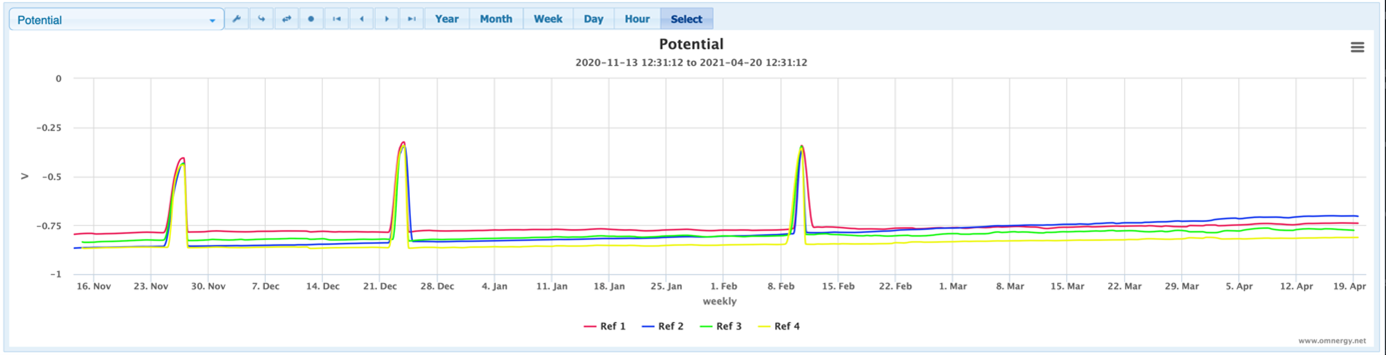
The system was provided with embedded reference electrodes and wired to enable performance evaluation as per the requirements of ISO 12696. Three battery powered web-based monitoring devices were used for remote system monitoring and performance assessment.
The initial performance data following 3 months of operation, identified that all 12 reference electrodes installed across the 6 anode zones met the 100mV depolarization criteria within a 24-hour period, as per the requirements of clause 8.6b of ISO 12696.
The anode to cathode current was recorded continuously and used to evaluate environmental effects and predicted an anode service life of over 20 years.